Belling machines play a critical role in plastic pipe manufacturing, particularly for PVC, UPVC, CPVC, and HDPE pipelines. Their function is simple but essential: they form a socket (or “bell”) at one end of a pipe, allowing it to be easily joined with another pipe or fitting without additional adhesives in many cases.
For manufacturers, understanding the step-by-step process of how belling machines work is vital for ensuring consistent product quality, high production efficiency, and compliance with international standards. In this article, we explain the working process in detail, highlight the technology behind it, and present supporting data to illustrate performance parameters.
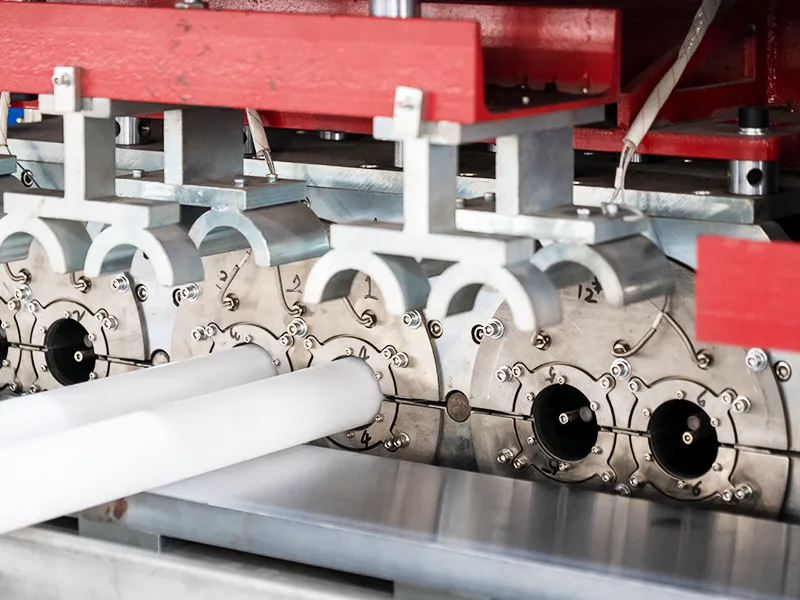
Overview of Belling Machines
Belling machines are designed to automatically heat, shape, and cool the end of a pipe to form a bell socket. The socket ensures strong, leak-free joints in water, drainage, and industrial pipes.
Key roles of belling machines in pipe manufacturing:
- Provide uniform and accurate socket dimensions
- Improve pipe connection strength and leak-proof reliability
- Reduce reliance on external couplings and adhesives
- Increase production speed with automated cycles
Types of belling machines commonly used:
- Automatic Belling Machines – Fully automated heating, shaping, and cooling.
- Semi-Automatic Belling Machines – Require partial operator input.
- Mandrel-Type Belling Machines – Use mandrels to shape the socket.
- Roto-Type Belling Machines – Rotate the pipe during heating for uniformity.
Step-by-Step Process of Pipe Belling
Step 1: Pipe Loading
The pipe is automatically or manually fed into the machine’s loading system.
Servo-driven clamps or pneumatic systems hold the pipe firmly in place.
Key requirements:
- Correct alignment to avoid deformation.
- Safe handling for thin-wall pipes.
Step 2: Pipe Heating
The pipe end is heated to soften the plastic material, usually using infrared heaters, hot air ovens, or contact heating systems.
Heating temperature typically ranges between 120°C to 140°C for PVC and 160°C to 180°C for CPVC.
Heating parameters table:
| Material | Heating Method | Temperature Range (°C) | Heating Time (sec) |
| PVC | Infrared / Hot Air | 120 – 140 | 20 – 40 |
| CPVC | Infrared / Hot Air | 160 – 180 | 25 – 45 |
| HDPE | Infrared / Hot Air | 120 – 130 | 30 – 60 |
Step 3: Socket Forming (Shaping)
A mandrel or calibration tool is inserted into the heated pipe end.
The softened pipe conforms to the mandrel shape, creating the bell socket.
Machines can create different socket types: Straight, Rigid, or O-Ring (with groove).
Types of sockets formed:
- U-Type Socket – Simple straight socket for solvent cement connections.
- R-Type Socket – Incorporates an O-ring groove for rubber sealing.
- Custom Socket – Tailored dimensions for specialized fittings.
Step 4: Cooling
After shaping, the socket is cooled to retain its form and prevent deformation.
Cooling methods include:
- Air Cooling: Fans blow cool air on the pipe end.
- Water Cooling: Spray or immersion cooling for rapid temperature drop.
Cooling comparison table:
| Cooling Method | Cooling Time | Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Air Cooling | 30–60 sec | Simple, low cost | Slower cooling, risk of deformation |
| Water Cooling | 15–30 sec | Faster, ensures shape retention | Higher energy use, needs water recycling |
Step 5: Pipe Unloading
Once cooled, the socketed pipe is automatically released and moved out of the machine via conveyor systems.
Finished pipes are stacked or transferred to the next production stage.
Control System and Automation
Modern belling machines use PLC and HMI panels for precise control of heating, shaping pressure, temperature, and cooling time.
Automation benefits:
- Reduced operator error
- Consistent socket dimensions
- Higher production rates
- Real-time monitoring and fault detection
Typical Performance Data
| Parameter | Value Range |
| Pipe Diameter Range | 50 mm – 630 mm |
| Socket Length Range | 60 mm – 300 mm |
| Cycle Time per Pipe | 40 – 90 sec |
| Machine Output | 400 – 600 pipes / 8 hrs |
| Power Consumption | 15 – 30 kW |
Quality Control in Belling
To ensure reliable pipe joints, quality control is critical:
- Socket Dimension Check: Diameter, depth, and roundness.
- Wall Thickness Consistency: Avoid thinning during heating.
- Leak Testing: Hydrostatic pressure test for O-ring sockets.
- Visual Inspection: No cracks, bubbles, or burn marks.
Advantages of Modern Belling Machines
- High Precision – Mandrel shaping ensures accurate socket size.
- Energy Efficiency – Advanced heating systems reduce energy use.
- Flexibility – Capable of producing multiple socket types.
- Durability – Heavy-duty design supports continuous production.
- Compatibility – Works with PVC, UPVC, CPVC, and HDPE materials.
Data-Driven Example: Production Efficiency
Let’s consider a manufacturer producing PVC pipes with a diameter of 160 mm.
Machine parameters:
- Cycle time: 60 seconds per pipe
- Working hours: 8 hours per shift
- Operator efficiency: 95%
Output calculation:
| Parameter | Value |
| Cycle Time | 60 sec |
| Pipes per Hour | 60 |
| Pipes per Shift | 480 |
| Effective Output (95%) | 456 pipes |
This data shows that even mid-capacity machines can produce 450+ pipes per shift, supporting large-scale supply chains.
Challenges in the Belling Process
Despite automation, manufacturers face some challenges:
- Overheating or Underheating – Leads to socket cracks or deformation.
- Mandrel Sticking – If cooling is insufficient, the pipe may stick to the mandrel.
- Uneven Wall Thickness – Results from improper heating or poor pipe alignment.
- Energy Consumption – High electricity usage if not optimized.
Preventive measures:
- Regular calibration of heaters
- Proper cooling system maintenance
- Routine inspection of mandrels and clamps
Innovations in Belling Machines
Manufacturers are introducing several advancements:
- Servo-Driven Systems: Precise positioning for faster cycles.
- Hybrid Heating Systems: Combination of infrared and hot air for energy efficiency.
- Automatic Pipe Sorting: Integration with extrusion lines for continuous operation.
- IoT Integration: Remote monitoring with smart alerts for predictive maintenance.
Belling machines are indispensable in modern pipe manufacturing. By following a step-by-step process of loading, heating, shaping, cooling, and unloading, they ensure that pipes are ready for secure and efficient installation.
From an industrial perspective, the adoption of advanced control systems, faster cooling methods, and automated handling not only boosts production efficiency but also guarantees consistency in quality. With increasing demand for infrastructure, water supply, and industrial piping, manufacturers investing in high-performance belling machines gain a significant competitive edge.