Belling machines are essential components in modern plastic pipe production lines, responsible for forming precise and durable bell ends on PVC, PE, and PP pipes. These bell ends ensure reliable jointing, watertight sealing, and efficient installation in plumbing, drainage, and infrastructure applications. However, like any industrial equipment, belling machines require careful operation and regular maintenance to sustain high efficiency and minimize costly breakdowns.
Understand the Working Principle and Structure
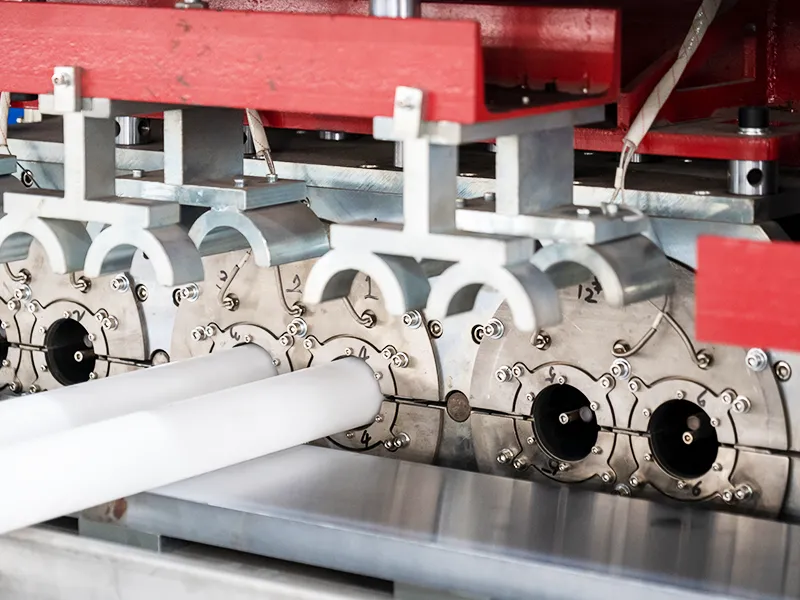
Before discussing maintenance, operators and technicians must understand how the belling machine functions. A typical automatic belling machine consists of several core units:
- Pipe Feeding System: Aligns and delivers pipes accurately to the belling station.
- Heating Oven: Softens the pipe ends uniformly to prepare them for shaping.
- Forming Unit (Mould or Mandrel): Shapes the heated pipe into the required bell configuration.
- Cooling System: Uses air or water to cool and solidify the newly formed bell.
- Ejection/Discharge System: Removes the finished pipe safely without deformation.
Knowing how these parts work together helps operators detect abnormalities early, adjust parameters accurately, and avoid misuse that could lead to premature wear or damage.

Implement a Strict Daily Maintenance Routine
Daily maintenance acts as the primary defense, preventing premature wear and extending machine lifespan. Simple tasks, when performed regularly, can significantly reduce downtime:
- Clean dust, plastic scraps, and residue from heating and forming areas after each shift. Accumulated debris can block sensors, reduce heating efficiency, or scratch the pipe surface.
- Wipe down sensors and photoelectric switches to ensure precise positioning and detection.
- Check the heating oven for carbon buildup or uneven temperature distribution. A clean oven ensures uniform pipe softening and prevents local overheating.
- Remove water accumulation from cooling sections and drainage points to avoid rust or leaks.
- Lubricate moving parts lightly according to the manufacturer’s guidelines to prevent metal-on-metal wear.
Establishing a simple, checklist-based daily routine encourages accountability among operators and prevents minor issues from becoming major failures.
Schedule Regular Inspection and Preventive Maintenance
While daily maintenance focuses on cleanliness and basic checks, scheduled preventive maintenance involves deeper inspection and replacement of wear parts at set intervals.
Key components to inspect regularly include:
- Heating elements and thermocouples: Replace aging or inefficient elements before they fail to avoid uneven heating or sudden shutdowns.
- Pneumatic and hydraulic systems: Check air lines for leaks, pressure fluctuations, and filter clogging. Inspect cylinders for wear and oil contamination.
- Forming moulds or mandrels: Look for wear, deformation, or surface damage that can affect bell shape accuracy. Polishing or replacement might be needed periodically.
- Guiding rails and bearings: Clean and re-lubricate to maintain smooth motion. Misalignment can cause abnormal friction and premature failure.
- Cooling systems: Check water pumps, spray nozzles, and circulation tanks for blockages or corrosion.
Many manufacturers recommend conducting minor inspections weekly, more detailed monthly inspections, and a comprehensive overhaul every 6 to 12 months, depending on production intensity.
Use the Right Operating Parameters
Incorrect temperature settings, pressure values, or cycle times can drastically shorten the lifespan of components such as heating elements, moulds, or sealing parts. Proper operating parameters should match the pipe material, diameter, wall thickness, and belling type (e.g., RING or SOCKET type).
Some tips include:
- Avoid overheating: Excessive temperatures accelerate oxidation and shorten the lifespan of heating elements. They can also cause material degradation and sticking to moulds.
- Control forming pressure carefully: Overpressure may stress pneumatic cylinders, deform mandrels, or crack heated pipes.
- Set reasonable cooling times: Insufficient cooling leads to bell deformation after demolding, while excessive cooling wastes energy and slows production.
- Adjust conveyor speed and feeding intervals to match the machine’s capacity. Overloading or irregular feeding causes mechanical stress and affects synchronization.
Documenting optimal parameters for different pipe specifications helps operators maintain consistency, reduces trial-and-error, and lowers the risk of component damage.
Train Operators Thoroughly
Operator skill plays a major role in extending machine life. Untrained personnel may unknowingly run the machine under improper conditions, overlook warning signs, or handle parts incorrectly during maintenance.
Effective operator training should cover:
- Machine structure and functions: Familiarity with each unit improves troubleshooting ability.
- Safe startup and shutdown procedures: Prevents thermal shocks and mechanical damage.
- Recognizing abnormal sounds, vibrations, or temperature fluctuations: Enables quick intervention before damage spreads.
- Basic maintenance and emergency response: Ensures operators can address small issues without waiting for technicians.
Many manufacturers offer operator training programs during installation and commissioning. Regular refresher sessions are equally important, especially when staff turnover is high.
Use Genuine Spare Parts and Consumables
Substandard spare parts may appear cheaper initially but often wear out quickly, cause poor performance, or damage surrounding components. For example:
- Low-quality heating elements may produce unstable temperatures or fail prematurely.
- Inferior mould materials may warp under high heat and pressure, leading to inaccurate bell dimensions.
- Unapproved lubricants might not withstand high temperatures, leading to increased friction and wear.
Always source parts and consumables from the original manufacturer or approved suppliers to maintain compatibility, safety, and longevity.
Maintain a Stable Production Environment
The operating environment greatly impacts belling machine durability. Key considerations include:
- Temperature and humidity control: Excess moisture can cause electrical short circuits, corrosion in pneumatic systems, and mould rusting.
- Clean, dust-free surroundings: Prevents particles from entering moving parts or contaminating pipes.
- Stable power supply: Voltage fluctuations can damage heating systems, PLCs, or sensors. Using voltage stabilizers or UPS systems is recommended.
- Proper air supply: Compressed air should be dry and clean. Install filters and dryers to protect pneumatic components.
A stable environment lengthens machine lifespan, improves product quality, reduces downtime, and significantly increases overall production efficiency.
Monitor Performance and Keep Records
Systematic record-keeping helps identify patterns, predict failures, and schedule timely maintenance. Modern belling machines often feature PLC systems with fault detection and data logging, but manual records are also valuable.
Suggested records include:
- Operating hours per day
- Temperature and pressure settings used for different pipe types
- Maintenance and inspection dates
- Component replacements and service history
- Breakdowns and corrective actions taken
Analyzing these records can reveal recurring issues (e.g., frequent heating element failures indicating power instability) and guide improvements.
Perform Timely Overhauls and Upgrades
Even with excellent maintenance, mechanical components have finite lifespans. Timely overhauls can restore the machine to near-new condition and prevent catastrophic failures.
During overhauls, inspect:
- Drive systems and gearboxes for wear or oil leakage
- Structural parts for cracks or fatigue
- Control systems for software updates or sensor calibration
- Safety systems for compliance with latest standards
Periodic upgrades — such as energy-efficient heating systems, improved control interfaces, or automatic lubrication units — can extend overall service life and improve productivity.
Adopt Predictive Maintenance Technologies
In recent years, predictive maintenance technologies have gained popularity in pipe processing lines. By adding sensors and monitors, manufacturers track real-time conditions to spot issues early.
For example:
- Vibration sensors identify bearing wear or alignment issues.
- Thermal sensors can identify overheating in motors or heating zones.
- Air pressure sensors can detect leaks or cylinder performance degradation.
- PLC data analysis can predict component failures based on usage cycles.
While predictive maintenance requires upfront investment, it significantly reduces unplanned downtime and extends machine life by enabling proactive intervention.
Address Issues Immediately
Small problems can quickly escalate if ignored. For example, a minor air leak might seem harmless but can cause pressure drops that strain the entire pneumatic system. A slightly misaligned mould can lead to repeated bell defects, increased scrap, and mandrel wear.
Establish a clear reporting and response system so operators can log issues immediately and maintenance teams can address them before they worsen. This culture of rapid response is critical for long-term machine health.
Belling machines are valuable assets in any pipe production line. Extending their service life requires a comprehensive strategy that combines proper operation, regular maintenance, skilled personnel, quality spare parts, and stable working conditions. By implementing daily cleaning routines, scheduled inspections, operator training, predictive maintenance technologies, and timely overhauls, manufacturers can maximize uptime, improve product quality, and achieve a stronger return on their equipment investment.
A well-maintained belling machine can operate efficiently for many years, supporting high-speed production lines and delivering consistent bell quality — ultimately giving manufacturers a competitive edge in the market.

